A guest post from Joe Wilson, reporting on the Cabinet Secretary for Education and Skills’ speech at the Scottish Learning Festival.
The Scottish Learning Festival is the annual gathering mainly of schools across Scotland. This year even had the usual mix of excellent keynotes and workshops to re-inforce changes across the sector and provide staff who can get out of school for one or two days with an important opportunity to network. Keynotes from the event are available here https://www.youtube.com/user/educationscotland
As well as a programme of talks there is an exhibition area featuring most of the agencies that support Scottish schools, commercial vendors, with a broad focus on technology, and a local authority village highlighting a range of initiatives across Scotland’s 32 local authorities.
Traditionally the event starts with an address from the Minister for Education and this year was no exception. There are usually too a couple of well-timed press releases or policy changes that appear on the morning of address to give speech some beef.
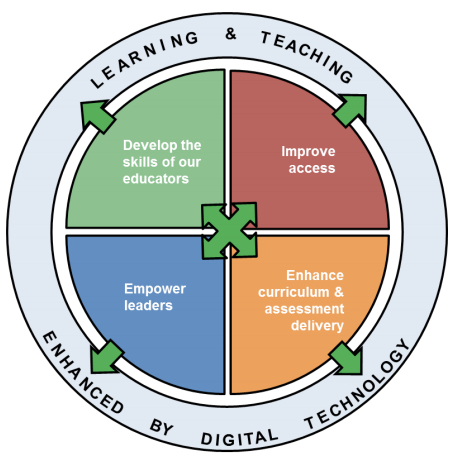
This year was the announcement that the ‘assessment burden’ in schools would be tackled (Government plans major changes to school qualifications) and the Digital Learning and Teaching strategy Enhancing Learning and Teaching Through the Use of Digital Technology was published the previous day.
I think I’ve attended all the SLF conferences and this was the most confident delivery I’ve seen by an Education Minister in the last 20 years, focusing unrelentingly on closing the attainment gap. It needed to be a confident speech, relationships are currently fragile across this sector and while the Minister has picked up his brief in a confident fashion, as ever with education, there is a fair amount of baggage to be dealt with.
So what happened?
Swinney’s speech was directive really; a call to arms for teachers, head teachers, local authorities and all those working in public education to focus on the core values of Scottish Education. The system is there to transform lives and should be underpinned by “wisdom, compassion, justice, integrity”. Scottish Education needs to build on its foundations and not rest on its laurels. There was reference to the recent OECD report on the state of Scottish Education; our report card is that we are on the right road but ‘could do better’ particularly around “closing the attainment gap”.
The challenge is that the right building blocks are there in our Getting it Right for Every Child, Curriculum for Excellence and Developing our Young Workforce policies, we need to free teachers and education leaders from unnecessary bureaucracy and let them get on with the job. The Minister praised the 23% rise in vocational qualifications now being delivered in schools as evidence of change happening and highlighted how the system was working towards building excellence and equity.
In his first six months Swinney has already taken action. Today, he announced that the assessment burden, the internal assessments in National 5, Higher and Advanced Higher, will go and be replaced with more externally assessed components. This has been done with agreement of the National Assessment and Qualifications Working Group. They are working through ways to give more resources directly to schools, but local authorities, head teachers and teachers also need to get rid of their own self-generated bureaucracy. Education Scotland is going to take down thousands of pages of guidance that is often contradictory. Definitive guidance is now provided here Delivering excellence and equity in Scottish education: A delivery plan.
The Minister’s speech did not directly address the Digital Learning and Teaching strategy and its actual or potential impact on the classroom. In response to questions, Swinney highlighted that connectivity was still a challenge in many schools and that resources were being allocated to improve bandwidth across Scotland and that schools should make more effective use of GLOW.
There is much that educational technology, or more specifically changes in educational practice supported by educational technology, could do to support the aim of closing the attainment gap in Scotland. Digital technology is to become central to all areas of curriculum, assessment and delivery.
Open Education has a key role to play in this but it is not explicitly referenced in the strategy. It as a key part in improving the relationship between teachers and learners and enhancing the learners’ experience.
I know for instance that SQA are looking to move towards making evidence digital a standard in all areas that it can – this could change face of assessment across Scotland. That is something that everyone across the education and skills system should be thinking about.
There was a question too about the support available for young learners with mental health challenges and the lack of re-sources and joined up provision from education, social and health services.
There was no mention in the speech around the external assessments that are being planned for primary and early stage secondary pupils to provide Government with a performance benchmark and nothing really of substance for those working in Colleges, Higher Education or the training provider sector.